Physiotherapy guide
Patients with pectus have poor posture, in addition to hinder the mobility of the chest increases the cosmetic deformity. With appropriate physical therapy techniques can improve posture thus improving mobility and respiratory function.
The Schroth technique (School of Barcelona) is a technique specific treatment for scoliosis that has an application in postural alterations.
In different starting positions, sitting, standing and lying, it is reaching progressive isometric tension of the muscles of the trunk, reaching a maximum correction.
In the case of pectus trying to achieve this correction both the sagittal and frontal plane while encouraging expansion in the anterior chest.
With the help of the therapist, the patient learns to tensions in areas targeted for increased chest expansion in sunken areas. This, together with a trunk autoelongación increases the mobility of the ribcage and decreases the collapse of the area. The relaxation of the diaphragm and manual therapy directed at improving the mobility of the chest increases the effectiveness of exercise and improvement of the expansion.
These are active exercises for the patient and directed by the therapist, which stimulates the correction orders and corrections passive trunk. It is also interesting the use of mirrors to assess posture and as a stimulus on the expansion of the chest.
A physical therapist trained in postural techniques can guide and teach the patient to improve posture and maintain it. Postural techniques are not easy to implement because they require a global correction of the position without allowing compensation that could be aggravating rather than correcting.
Here are several exercises that can help improve the position but it is recommended that initially be monitored by a professional.
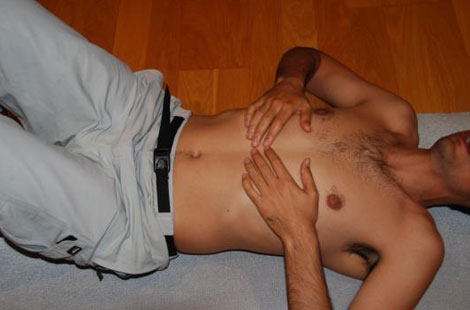
1. Diaphragm relaxation exercise
The diaphragm is the main respiratory muscle, hemicúpulas forms two (right and left) that separates the chest from the abdomen. It is a flat muscle with a central tendon and a fibrous portion also has a few pillars of integration into the spine. Muscle fibers have an insertion around the costal margin which is where you will enter the muscle to relax. The relaxation of this muscle will improve the mobility of the chest and allow better postural correction.
The exercise consists of 3 maneuvers performed in expiration and in any case have to be painful:
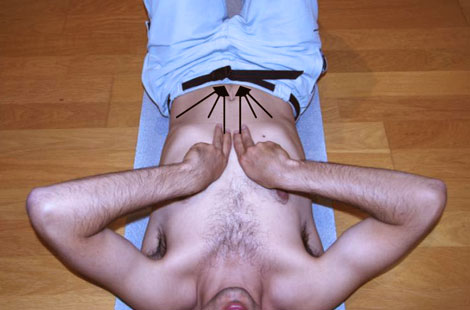
The position of the patient is lying face up with legs bent so that the entire spine is relaxed and resting on the ground.
A. Massage:
- Place both hands under the ribs in the center of the chest, performed the exercise with the pads of the fingers.
- It is a gentle massage in circles from the central area to the side along the ribs until they are accessible.
- The massage is done as you exhale, the air is not taking nothing and making empty goes round the gentle pressure.
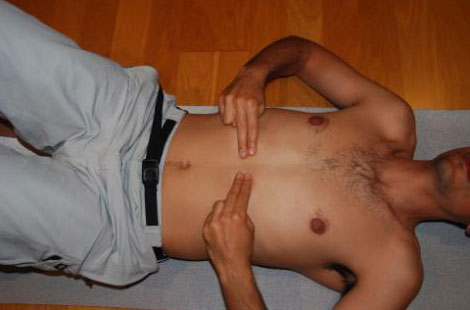
B. Pass on the skin:
- As previously placed both hands below the ribs in the center of the chest but are now used on 2 and 3 finger.
- From the center toward the sides does a "line" parallel to the ribs by a gentle pressure.
- 3 repetitions were performed during expiration.
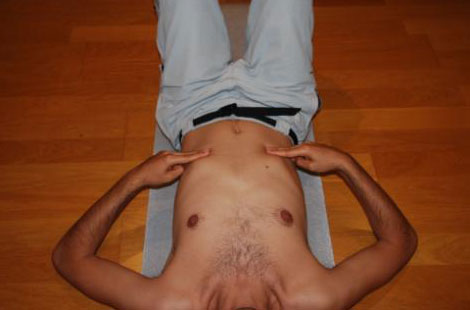
C. Passes over the abdomen:
- On 2 and 3 fingers of both hands are placed below the ribs, but now directed towards the navel.
- 3 lines are made perpendicular to the ribs that converge in the navel. The first line from the center, the next part of half of the ribs and the third end portion of the ribs. As if you drew a "fan" in the abdomen.
- The three lines are made during expiration.
After this exercise it is interesting to feel the change in breathing and freedom of the rib cage. In addition to improving the perception of the sunken or concave is important to mentally visualize the area and feel their mobility and expansion. This is useful for the patient place one hand on the area and trying to note that this mobility mobility is increasing. A good way to visualize the area is to imagine that a balloon inside the chest and breathing to be inflated after breathing if hand also noticed an increase in mobility is a very useful and enjoyable exercise.
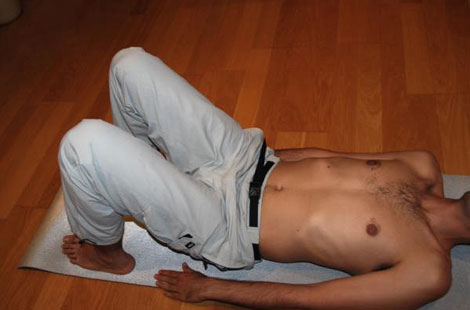
2. Self-mobilization exercise cage.
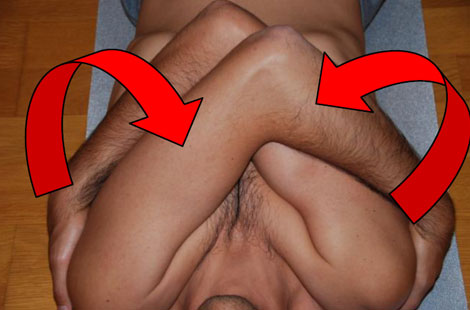
- The patient is lying in the same position with knees bent.
- These embrace the blades and go making a swing to and fro noticing how they move the ribs.
- Hands are taken down from the shoulder blades and continues to this roll.
The movement is slow and relaxed rib being aware of the movement in each area so that the emphasis is on areas where the movement is more difficult. In this exercise is not taken into account as previously breath but feel the change is recommended after exercise.
3. Self-stretching exercise.
This exercise is based on the ability of the trunk to reach a self-stretching sagittal curves thus improving posture and appearance. Exercise is more complicated and may be performed in different positions: lying, sitting and standing.
Here we describe the exercise only in face-up position because this position is referenced to the ground and this facilitates the exercise. The other two positions are very difficult to execute if they are guided by a professional.
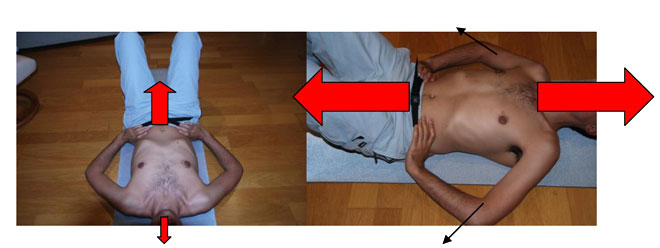
- The position of the patient remains lying with legs bent and relaxed throughout the column resting on the floor. The hands are placed in the pelvis and elbows on the floor without pressure.
- The patient takes a few minutes to feel the breath and focus your attention on the sunken feeling and increasing their mobility, "as if to fill up a balloon."
- Starts self-sustained stretch the pelvis fixed by a mild contraction of abdominal muscles, taking care not to increase the pressure in the lower back down.
The idea of fixed pelvis can be increased by a slight palm rest down to the feet. Keeping this what it is, breath after breath, go away the head relative to the pelvis thus achieving the stretch.
You can increase the feeling of stretching to improve chest expansion taking elbows out axially, which also stretches the muscles of the upper limbs and chest.
The exercise is rapidly increasing, at no time is left to stretch. Thus the muscle adapts to stretching, is healthier and lasting muscle.
As in previous years we used to breathe. When you catch air stabilizes the position, and the empty stretches but always maintaining or increasing the above if possible. It is important to the initial display of the sunken and maintain the sense of expansion in the area throughout the year.
As mentioned above this exercise is not easy to implement so it is advisable initially a professional guide.
The order of the exercises also have an interest because the previous work of initial relaxation of the diaphragm and rib cage movement easier after the third year.
Once the exercise using a mirror to assess the change in posture helps improve and stabilize the perception both of mobility in the sunken looking ahead, looking like the side view.
With help from the therapist, the patient learns to tensions in areas targeted for increased chest expansion in sunken areas. This, together with a trunk autoelongación increases the mobility of the ribcage and decreases the collapse of the area. The relaxation of the diaphragm and manual therapy directed at improving the mobility of the chest increases the effectiveness of exercise and improvement of the expansion. They are active exercises for the patient and directed by the therapist stimulates the correction orders and corrections passive trunk. It is also interesting the use of mirrors to assess posture and as a stimulus on the expansion of the chest.